Technical Architecture
Overview of YuLan-OneSim's system architecture and technology stack.
System architecture
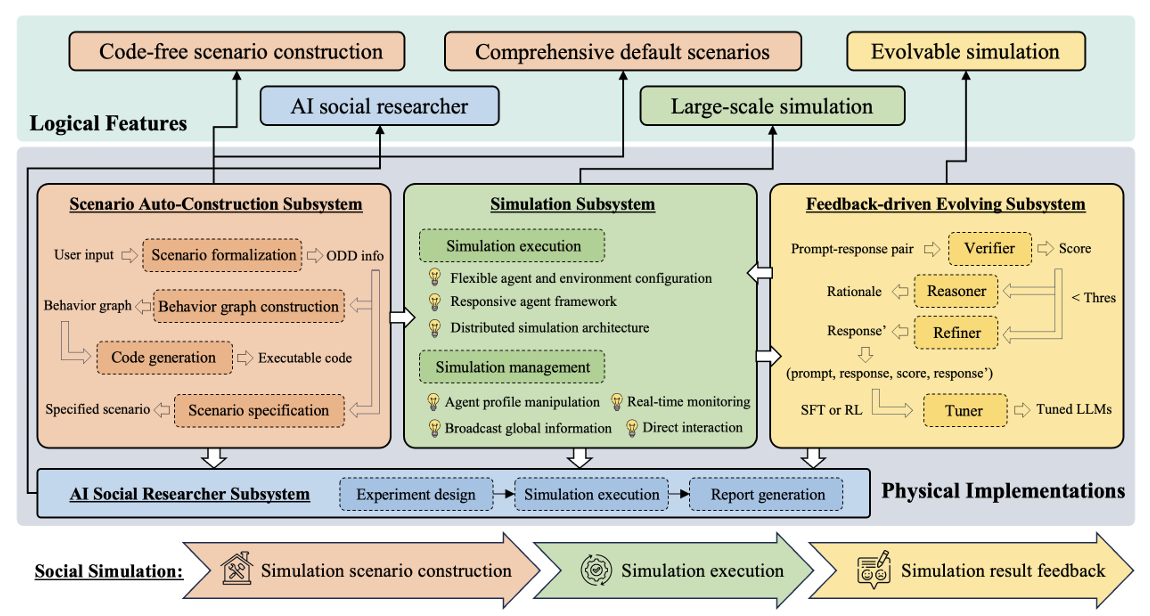
Scenario Auto-Construction Subsystem
- Function: Converts natural language descriptions into executable simulation code.
- Key Components:
- ODD Protocol Translator: Uses the Overview, Design Concepts, and Details (ODD) protocol for formalizing simulation models.
- Behavior Graph Construction: Models agent behaviors and decision-making logic via a structured graph.
- Code Generation Engine: Automatically generates simulation code based on user input.
- User Interface: Allows users to define scenarios using natural language prompts or templates.
Simulation Subsystem
- Function: Executes and manages large-scale simulations with real-time monitoring.
- Architecture:
- Fully Responsive Agent Framework: Enables dynamic, event-driven interactions between agents and environments.
- Distributed Master-Worker Architecture: Scales up to 100,000 agents by distributing computational load across multiple nodes while maintaining global consistency.
- Simulation Execution Engine: Manages agent actions, environment updates, and interaction logic.
- Features:
- Real-time visualization of simulation events.
- Flexible configuration of agent profiles, population sizes, and environmental parameters.
Feedback-Driven Evolving Subsystem
- Function: Improves simulation realism through feedback integration (from AI or humans).
- Framework:
- VR²T Framework (Verifier–Reasoner–Refiner–Tuner): A multi-agent mechanism that evaluates simulation results, identifies issues, and fine-tunes the LLM backbone.
- Supports both automated error correction and human-in-the-loop refinement.
- Goal: Ensures continuous improvement and alignment with expected behavioral patterns.
AI Social Researcher Subsystem
- Function: Automates the end-to-end social science research process.
- Modules:
- Experiment Design Module: Formulates hypotheses, selects scenarios, and configures simulations.
- Report Generation Module: Analyzes simulation outputs and generates technical reports in LaTeX format.
- Workflow:
- User inputs a research topic.
- The AI researcher formulates questions, designs simulations, runs them, and interprets results.
- Generates structured reports with visualizations, analysis, and conclusions.